Practical analysis of K-REACH regulations shows that the key points of compliance are coming
South Korea's K-REACH regulations (that is, South Korea's Chemical Registration and Evaluation Act) have been officially and fully implemented on January 1, 2015, as another chemical management act with international influence, will have a huge impact on the global chemical industry, including Chinese chemical enterprises. At the same time, the Ministr
Korea K-REACH regulation (that is, the Korean Chemical Registration and Evaluation Act) has been officially and fully implemented on January 1, 2015, as another chemical management act with international influence, will have a huge impact on the global chemical industry, including Chinese chemical enterprises. At the same time, the Ministry of Environment (MOE), which is responsible for enforcement, together with the National Institute for Environmental Research (NIER) and the Korea Chemicals Management Association (KCMA), has published a series of important K-REACH implementation rules, technical guidelines and lists of related chemicals to help companies, agencies and authorities better understand and respond to the regulations.
It should be noted that the official information released by South Korea is currently only in Korean, which brings great obstacles for Chinese enterprises to obtain regulatory information in a timely manner.
As a new chemical registration management regulations, South Korea's K-REACH regulations are different from the EU REACH regulations in terms of substance information confidentiality, registration exemptions, and easy registration of new substances, and some requirements are even more stringent.
K-REACH Regulatory Obligations and Concerns
For the protection of trade secrets, Chinese export enterprises to South Korea must designate qualified OR (Only Representative, the concept is the same as that under the EU REACH regulation) to conduct entrusted operations when fulfilling the corresponding legal obligations. According to K-REACH regulations, the main obligations that relevant enterprises need to fulfill are shown in Table 1.
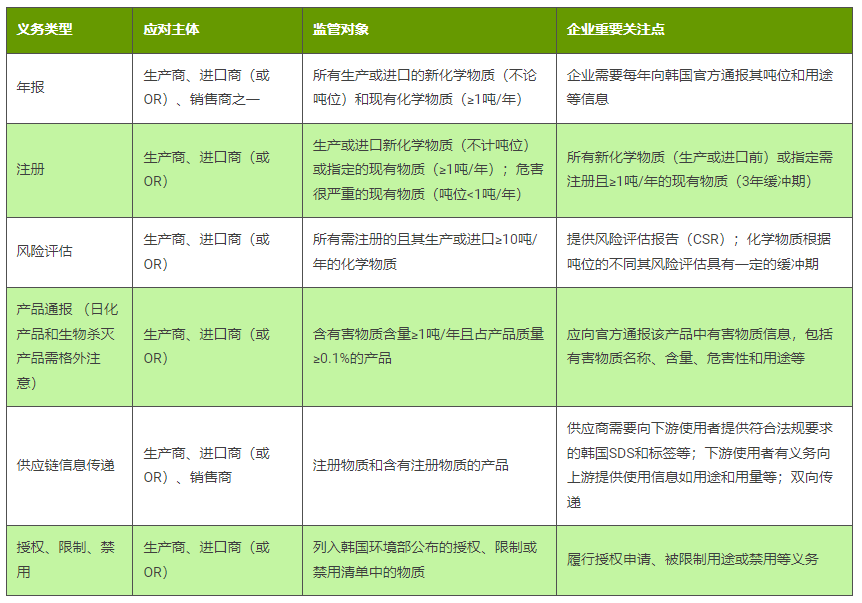
K-REACH confidential application, what do you know?
Most companies will first consider the cost before K-REACH regulations, and companies are also very concerned about whether product information will be leaked, whether the basic material information or importer information will be known by competitors, from a commercial point of view, not every company is willing to disclose their material information. Therefore, in full consideration of the interests of the enterprise, the in-depth analysis of the provisions related to confidentiality in the regulations, in the annual report, registration, exemption confirmation, product notification and other application forms have designed the necessary confidentiality options, hoping to ensure the business confidential information.
According to Article 45 of the K-REACH regulation, when the applicant provides the data in accordance with the corresponding provisions of the annual report, registration, exemption confirmation, product notification, risk assessment, if the purpose of protecting the confidentiality of chemical substances is to apply for data protection, the Ministry of Environment shall not disclose the relevant information within the data protection period (15 years) stipulated by the Ministry of Environment order. There is no fee for confidentiality requests.
According to the actual submission experience, the contents of the application for confidentiality under different obligations are the same. However, when applying for confidential declaration and importer information under K-REACH, OR information will be used as a substitute for publication. At the same time, the K-REACH regulation also stipulates that if the information applied for confidentiality is already public information at home and abroad, it is not applicable to the confidentiality application. For example, if the substance that applies for confidentiality has disclosed the substance (pre-registration) information such as the substance name, CAS number, etc., under EU-REACH, then the substance is considered to be publicly available information abroad, and the confidentiality application is not accepted.
K-REACH confidentiality application process is different from EU-REACH regulation. Firstly, substances applying for confidentiality need to be identified by SIP (substance identification profile), but not by spectrogram. STN retrieval is usually used as SIP identification method. STN search can help the applicant to create an alternative class name of the confidential substance that meets the requirements, and it can also know whether the intended confidential substance has been disclosed at home and abroad. Secondly, if the confidentiality requirements are met, a compliant class name can be created in accordance with the guidelines for Material Alternative class names. Finally, complete the confidentiality application form and submit it together with other declaration materials to the appropriate competent authority, NIER, KCMA or REO. After the official approval is passed, the class name and OR information published on the official website are confidential.
K-REACH registration exemption, have you paid attention?
The scope of K-REACH regulation is the chemical substance itself, including simple substances, substances in preparations, or substances intentionally released in articles. K-REACH clearly stipulates that for all new substances and designated registered existing substances with tonnage higher than 1 ton/year, unless K-REACH regulations do not apply or can be exempted, K-REACH registration is required, otherwise it cannot be produced or imported in South Korea. Under K-REACH regulations, exemptions exist in the following cases: 1) substances are completely exempted and regulated by other regulations (such as agricultural pesticides); 2) Direct exemption from certain provisions of K-REACH regulation (such as polymer monomers); 3) You need to apply for an official confirmation of exemption to be exempt from registration (such as PLC exemption). Among them, the judgment of exemption from registration is directly related to the cost and cycle of compliance response of enterprises, and whether K-REACH obligations can be correctly fulfilled. So which substances or products do these three exemptions specifically target?
Substances fully exempt from K-REACH regulation and regulated by other corresponding regulations include radioactive substances, pharmaceuticals and active substances, cosmetics and raw materials, pesticides and active substances, pesticides and fertilizers, food and additives, military substances, health functional foods and medical devices. It should be noted that if the substances produced or exported are used as pharmaceutical intermediates or biocides, they cannot be exempted and need to fulfill the obligations related to K-REACH.
According to the exemption provisions of Articles 8 and 11 of the K-REACH regulation, if the substance is imported with the device, used for the trial operation of the device, contained in the product that plays the function in a fixed form and will not be released during use, and used for investigation and research, it can be directly exempted and does not need to fulfill the relevant obligations.
In particular, chemical substances that need to apply for exemption confirmation are worth mentioning. Such substances need to be judged in conjunction with their use and even the process. The details are as follows:
Manufacture or import of chemical substances not exceeding 10 tons per year, all for export;
for scientific research or analysis of chemical substances in reagents;
Chemical substances for the purpose of research and development to improve the product, improve the production process, test use, medium (small) test;
non-separated intermediates;
separable intermediates that do not release and expose to the human body or the environment;
A list of substances of non-toxic or low concern published by ministerial order;
Low Concern polymer (PLC).
The exemption application of overseas enterprises in Korea needs to entrust OR, and provide the relevant information required for the exemption application, such as company information, importer information, basic material information, use description information, etc., and finally submit it in the form of a file. After the official assessment is passed, an exemption confirmation notice can be issued before the enterprise can start production or import.




 Consultation
Consultation
 400-115-9001
400-115-9001